RoboTwin Series New Release: Open-Source Large-Scale Domain Randomization Dual-Arm Manipulation Data Synthesizer and Benchmark}
RoboTwin 2.0 introduces an open-source domain randomization data generator and benchmark for dual-arm manipulation, enhancing robustness and generalization in robotic tasks.


Author: Tianxing Chen, TianxingChen.github.io, PhD student at HKU MMLab, supervised by Prof. Luo Ping. Published multiple papers at top conferences, awarded ECCV Best Paper, CVPR Highlight, and more. Organizer of CVPR 2025 RoboTwin Competition. Co-founder of Lumina Embodied Intelligence Community.
Recently, Shanghai Jiao Tong University ScaleLab and HKU MMLab@HKU released RoboTwin 2.0 and a technical report on the dual-arm collaboration challenge at CVPR. RoboTwin 2.0 open-sources a large-scale domain randomization data generator and a benchmark set with 50 tasks, sharing winning solutions and insights from the competition.
The first authors are PhD students Tianxing Chen (HKU), with corresponding authors Prof. Mu Yao (SJTU ScaleLab) and Prof. Luo Ping (HKU). Co-first authors include Zanxin Chen, Baijun Chen, Zijian Cai, Yibin Liu, among others.
RoboTwin 2.0 introduction video:
RoboTwin series has been featured as CVPR 2025 Highlight, ECCV 2024 MAAS Workshop Best Paper, and as official challenge topics at the 19th “Challenge Cup” AI + Challenge Competition, CVPR 2025 MEIS Workshop, and Zhangjiang Humanoid Robot Innovation & Entrepreneurship Competition. It has also gained 1.2k stars on GitHub.

- Paper Title: RoboTwin 2.0: A Scalable Data Generator and Benchmark with Strong Domain Randomization for Robust Bimanual Robotic Manipulation
- Project homepage: https://robotwin-platform.github.io/
- Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.18088
- Code repository: https://github.com/RoboTwin-Platform/RoboTwin
- User documentation: https://robotwin-platform.github.io/doc/
Introduction
Dual-arm robots play a vital role in complex tasks like assembly, tool use, and object transfer. However, training general operation strategies faces bottlenecks: high cost and time for real data collection, lack of scalable expert data generation in simulation, and insufficient domain randomization to simulate real-world complexity. Additionally, behavioral differences across platforms hinder generalization.

To address this, RoboTwin 2.0 introduces a multimodal large model-based simulation in-the-loop expert code synthesis, open-sourcing a RoboTwin object dataset (RoboTwin-OD) with 731 objects across 147 classes, richly annotated with operation points, directions, and semantic info. It supports 5 body types and 50 tasks, with domain randomization to enhance robustness against unseen environments. The data generator and benchmark set are built upon these methods, demonstrating significant improvements in model robustness and generalization.
Methods
1. Expert Code Generation
RoboTwin 2.0 introduces a streamlined API library to lower the code generation barrier for multimodal models. Combining keyframe visual observations and real-time feedback, it iteratively refines task expert code, improving accuracy and efficiency.

2. RoboTwin-OD (Object Dataset)
To create diverse simulation data covering more skills and objects, RoboTwin-OD includes 147 classes and 731 instances, with 534 generated via AIGC and convex decomposition, and others from Objaverse and SAPIEN PartNet-Mobility. Each object is annotated with multiple operation points, directions, and semantic info, supporting complex scene design and large-scale task synthesis.
3. Adaptive Grasping for Different Platforms

Due to kinematic and structural differences, different robotic arms have varying reachable spaces and preferred grasping directions. RoboTwin 2.0 constructs a candidate set of grasping approaches for each object, combining optimal approach directions, random pose perturbations, and parallel motion planning, supporting 5 body types.
4. Domain Randomization
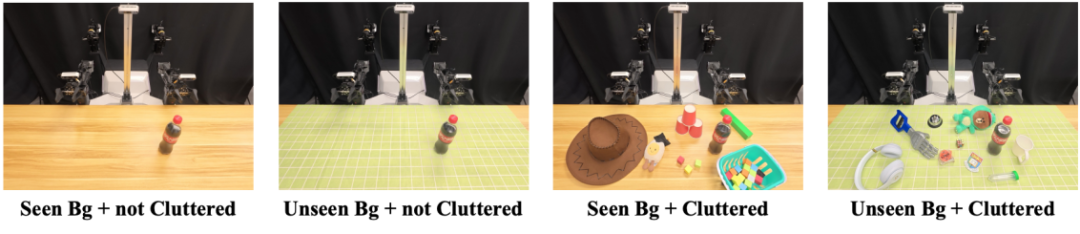
To ensure robust performance in complex real-world scenarios, RoboTwin 2.0 employs systematic domain randomization across multiple dimensions: cluttered scenes, diverse textures, lighting variations, tabletop heights, and language instructions. This extensive randomization enhances model robustness and generalization.
In cluttered scenes, random objects are placed to simulate interference; textures are generated from a large library of 12,000 high-quality samples; lighting conditions are randomized; tabletop heights are varied; and language instructions are automatically generated with diverse templates and object descriptions, improving the model’s ability to handle unseen commands.
5. RoboTwin 2.0 Data Generator and Benchmark
Supporting 5 body types and 50 tasks, the data generator produces diverse, domain-randomized simulation data, enabling robust training and evaluation.
Experimental Results
1. Closed-Loop Expert Code Generation Performance
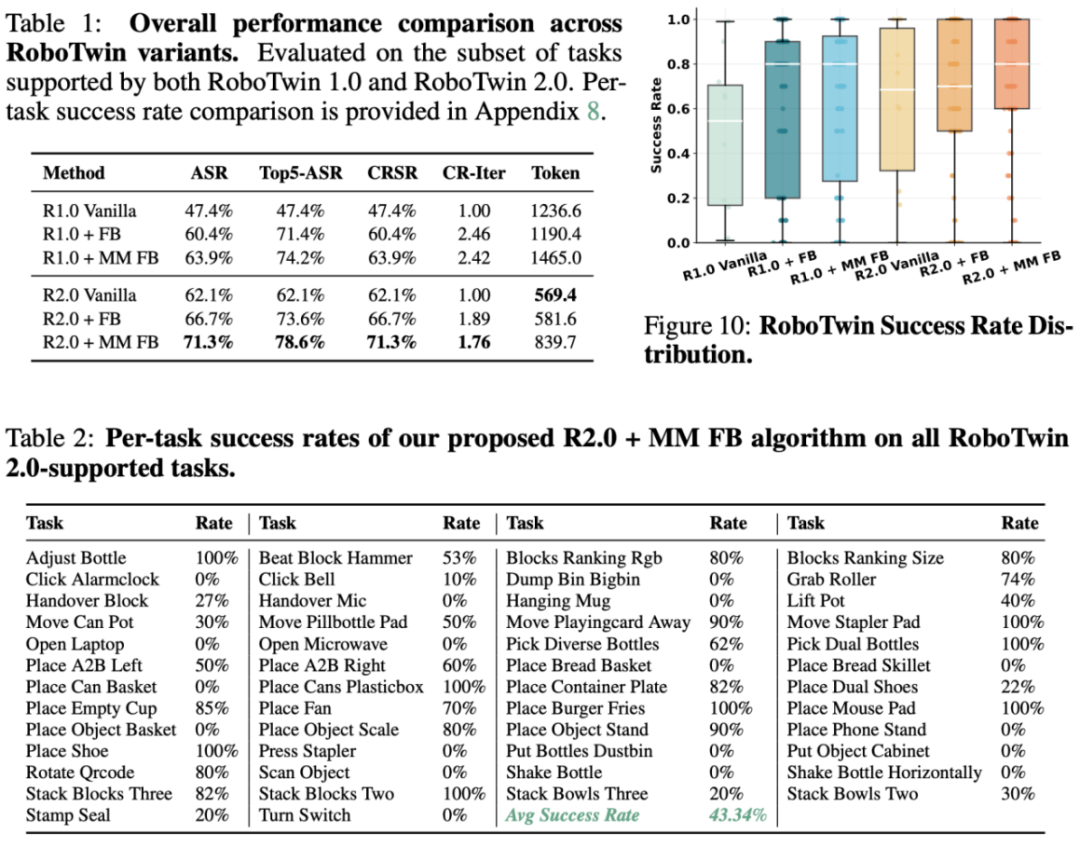
Compared to RoboTwin 1.0, without skill addition, RoboTwin 2.0’s average success rate (ASR) and top-5 ASR on 10 typical tasks increased from 47.4% to 62.1%. With structured feedback, ASR further rose to 66.7%, and multimodal feedback reached 71.3%. Iteration count decreased from 2.46 to 1.76, and token consumption was significantly reduced.
2. Enhanced Adaptive Grasping
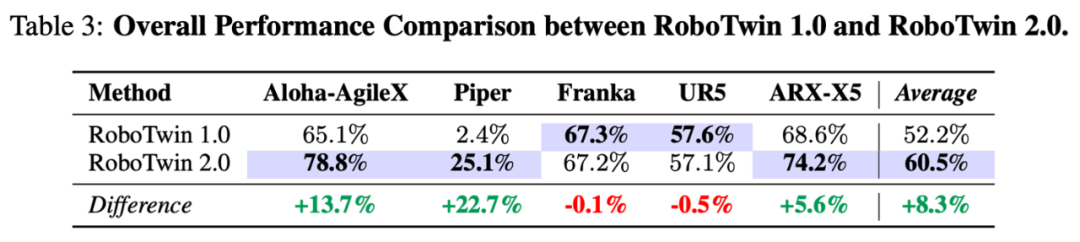
On five dual-arm platforms, RoboTwin 2.0’s data synthesis success rate improved by an average of 8.3%, with larger gains on lower DoF platforms: +13.7% on Aloha-AgileX, +22.7% on Piper, and +5.6% on ARX-X5.
3. Impact of Domain Randomization on Strategy Robustness
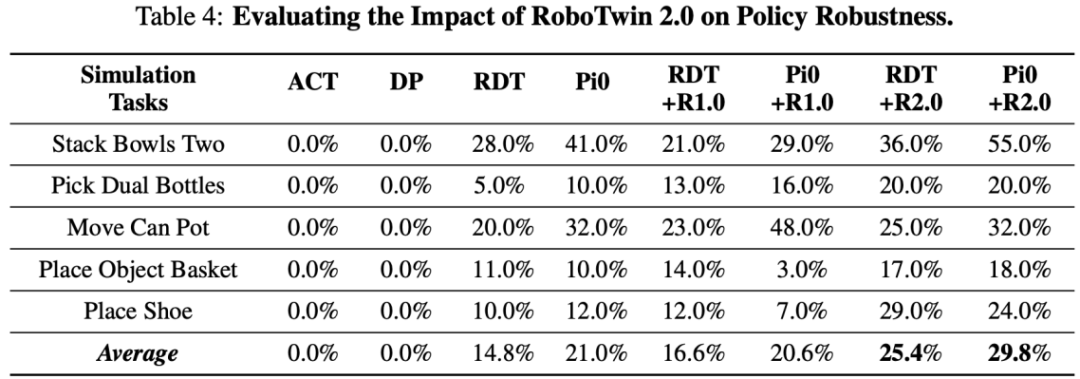
In ablation experiments with VLA framework, fine-tuning large pre-trained models RDT and Pi0 on 9600 domain-randomized samples improved performance on unseen tasks by 10.6% and 8.8%, respectively, demonstrating strong generalization.
4. Zero-shot Transfer in Real World
In four real dual-arm tasks (Bowls Stack, Block Handover, Bottle Pick, Bell Click), models trained with 1000 RoboTwin 2.0 synthetic trajectories achieved success rate improvements of 13.5%, 27.5%, 23.5%, and 33.0%. Even without real data, zero-shot performance increased by 21.0% and 20.5% in background scenarios, demonstrating strong sim2real transfer capabilities.
These results showcase RoboTwin 2.0’s comprehensive advantages in code generation, environment robustness, and sim2real transfer, providing a solid foundation for future large-scale, scenario-rich dual-arm manipulation research.
Open Source

We open-source RoboTwin 2.0 code for 50 tasks, over 100,000 pre-collected domain-randomized operation data, the full RoboTwin-OD semantic asset library, and user-friendly documentation.
RoboTwin CVPR Challenge Technical Report
64 teams participated, with over 400 individuals. The top teams include Tsinghua-Horizon’s real robot champion and JD.com’s simulation champion. The report shares key algorithms like SEM and AnchorDP3, and insights on data quality, preprocessing, language robustness, multimodal fusion, and model architecture for dual-arm manipulation.